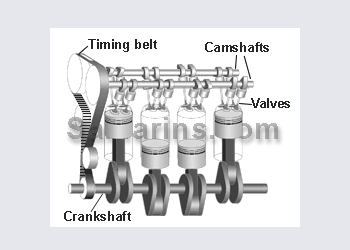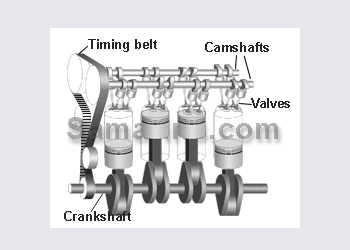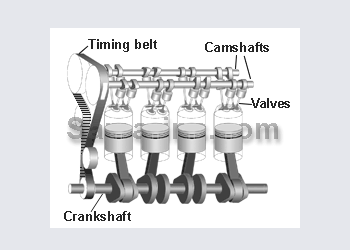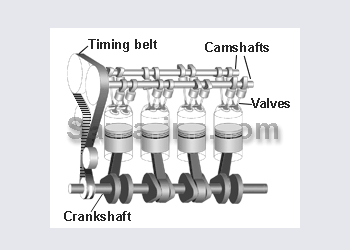
Toyota 4 A-FE. 1600
To start we split the head from the block because we were working in pairs.
Cylinder head
once everything is dismantled and in order it is imortant to measure each component (if it is not visibly damaged) this is because the parts inside an engine have all got clearences.
cylinder head itself
we visually inspect the head to make sure that is not scored, pitted, chipped or worn. We check for these signs of damage because pitting and scoreing could cause a build up of carbon causing excess heat, if it is worn through to the water jacket a loss of compression can occur.
once the visual inspection is done run a straight edge over the surface to determine if the head is twisted or warped, if it is planeing can rectify the problem to an extent otherwise it is a throw away job.
 valve stems to valve guides
valve stems to valve guides
the reason why we make sure that the clearences are within specifications is because oil will be able to travel freely to and from the head to the piston bore, it also means that the valve could sit unevenly on the seat if the stem guids are worn to much. We also check the stems for bending and wear visually and with vernier guages, we also check the springs and collets to see if they are in good opperating condition otherwise the valves may not be pulled onto the seat hard enough or fast enough.
 Cam shaft
Cam shaft
Like the other components the shafts are visually inspected for wear, bending and corrosion but because it is hard to visually check the lobes for wear so we use a micrometer and we messure from the base to the nose because if it is worn to much the valve timing will be out.
Another thing to measure on the camshaft is the journels these are checked with a DIT guage which determines if there is any ovality or twist in the camshaft - both of which would effect how even the spin of the shaft is.
The camshaft bearings have to checked with a plasti-gauge to determine whether or not the gap is suficient to allow for lubricating oil to travel through the slot to be transfered onto the shaft, this is because of the huge amount of friction/heat. An important thing to know when it comes to the oil grove is that it increases in width as it is torqued down.

 Camshaft valve buckets
Camshaft valve buckets
The valve buckets in this particular engine run with a pad of a certain thickness on the top of the bucket, the thickness of the pad determines how far the valve spring is compressed and how far the valve itself is opened. It also means that if wearing occurs it wears the pad which is easily replaced and not the whole bucket.
 Cylinder block
Cylinder bore
Cylinder block
Cylinder bore
We visually check the bore for pitting and scoring then we measure it in 6 different places within the bore these measurements when woked out tell us how much ovality and taper is in the bore from the stress the piston puts on the block especially on the thrust side.
 Piston
Piston
-Again visually inspect for wear, check the piston rings are all intact.
-Measure the piston on the trust sides just above the skirt to determine how much wear has occured and compare it to the secifications.
-Measure the gap between the ends of the piston rings to make sure that they are going to hold compression from entering the crank shaft housing.
-The conrods need to be checked on a special straight edge tool to see if they have been bent or twisted because if they are damaged they will put unnecessary stress and force on the conrod bearings and crankshaft.
 Crankshaft
Crankshaft
Once we have inspected the crankshaft for damage we check the journals for runout using the DTI guage, the crankshaft has to be very strong to accomodate for 4 pistons running on top of it so it has to be turning exactly true within the bearings.
 Important to remember
Important to remember
Always torque the crankshaft bearings, conrod caps and head in sequence and to specifications.






.jpg)