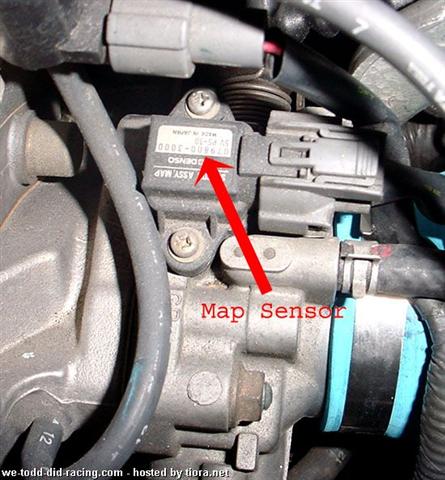
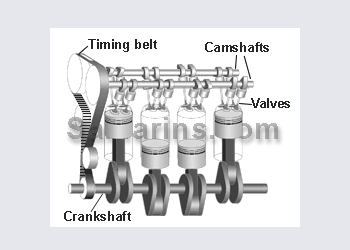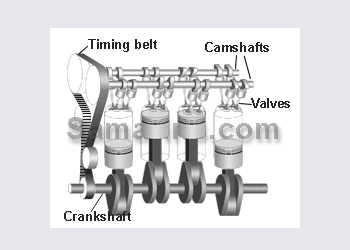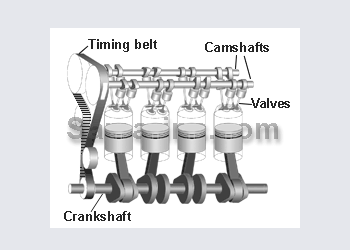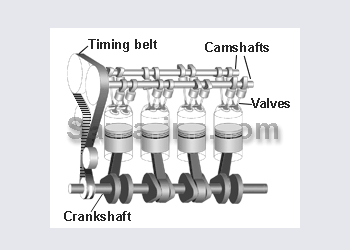
An inertia starter motor works by throwing the pinion into mesh with the fly wheel at high speeds causing the engine to turn over. this is achieved by electrical current flowing through the magnetic shoes causing the armature to spin which then throw the pinion into gear. Once the pinion has forced the fly wheel into rotation the side of drive would change, making the pinion clutch engage retracting the pinion.
Pre-engaged starter
This starter works and relys on the solinoid which uses a lever/linkage to enguage the pinion before it starts to spin, this system means that there is minimum wear on the teeth.

Alernator
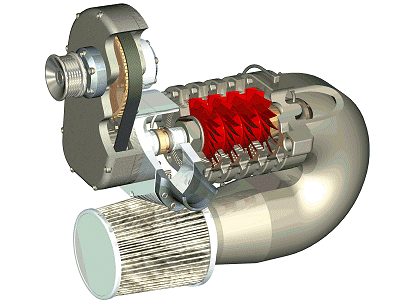
An alternator is an electromagnetic unit that is driven by a belt from the motor this means it wont run under its oun power. This is a rotor that cuts the magnet feild made by the coil and shoes, it turns within a stationary set of conductors called a stator. As the rotor is driven it cuts through the magnetic field causing the current to change producing an alternating current. This current changes due to the different polarity of each side of the magnet. This current is then feed through a rectifier which stabilises the voltage to a direct(DC) current. The alternator is used to power the electrical systems of the engine once started and charge the battery so it produces around 14 + V





.jpg)