Explain the terms ( Kinetic energy) Conduction,convection and radiation? Conduction is heat energy moving through a solid e.g. steel. Convection is the cycle ov heat through a liquid as the hot liquid rises the cold falls. Radiation is heat being transfered to the air from a hot object e.g. the engine
Indirect cooling? The coolant is in a closed cycle but still uses the raw water to cool the coolant further, this is a effective way of heat control because it works the same way as a car engine on a thermostat which means less corrosion and a faster warm up.
Direct cooling? The direct cooling method is to pump raw water up and through the water jacket then back out with the exhause fumes, this isnt as effective or practicle as indirect because of the corrosion and how long it takes for the engine to heat up - costing you more fuel.
What are the the problems you get with indect and direct cooling? Corrosion is the biggest problem because the raw water is so destructive, maintanance on the indirect cooling can be a mission - depending on how easy it is to get to the heat exchanger. You also have to regularly check the inlet valves because the can get blocked - causing over heating.
What is the puppose of a thermostat? To allow the engine to heat up to optimum running temp before letting the coolant pass through to be kept constant so the engine is always at the right temp.
Pressure cap? The pressure cap is a release valve for when/if the pressure in the radiator becomes to high for the specifications, it is also the way to top up the coolant.
Why is engines fitted with a core plug, and what is the purpose of a core plug? The manufacturors put them in so when they are moulded the can shake out all the core moulding sand. another reason for the core plugs is so if the water in the water jacket freezes it won't crack the block or head it will push out the frost plug instead.
What is the purpose of a heat exchanger? A heat exchanger is the equivelant to a radiator on a car except instead of cooling the coolant with air you cool it with raw water from the ocean which is also cycled to keep cold. It works by raw water circulating through pipes next to the circulating hot coolant the heat is transfered to the raw water leaving the coolant colder.
What is the core of the heat exchanger made of? Aluminium or copper because they are light weight and dont corrode very easily.
How does the centrifugal circulating water pump work?
How does a raw water pump work?
Why is it important to lubicate the impellor when fitting from new?
When fitting a impellor what should you check before refitting the housing and why?
What is the purpose of a oil cooler and how does it work?
What is the process of a intercooler/aftercooler how does it work?
Why do we have Inhibitors & antifreeze?
How do you test Antifreeze?
What is cavitation corrosion?
What is galvanic corrosion?
Describle the terms
Stray corrosion?
Stress corrosion?
Corrosion Fatigue?
Crevice corrosion?
What is Electrolysis?
How do you prevent corrosion?
Why and what is bonding in the marine industry?
What are sacrifical anode made off?
Where would you place them in the marine industry?
10.06.11
What is the purpose of a water muffle?
Wednesday, June 29, 2011
Tuesday, June 28, 2011
2 - STROKES
What is happening below and above the piston?
Explain what is meant, by scavenging when applied to 2 stroke SI engines?
Why must roller and ball race bearings be used on 2 stroke SI engine crankshafts?
Why are rollers caged in crankshaft bearings?
Why must ‘split’ type bearings be used on one piece crankshafts?
Why do we have pins between the piston ring gaps on a 2 stroke?
How does a reed valve work on a two stroke?
How do you check a reed valve?
Explain the term ovality and taper and how are they formed?
How does the piston rings seal in the bore?
What is meant by the terms groove depth, side clearance and end gap on the pistons rings?
Explain the difference between a 2 stroke and a 4 stroke engine?
What is meant by each of the following terms:
(a) Mechanical Efficiency(b) Thermal Efficiency(c) Volumetric Efficiency?
List 2 methods of lubricating the internal parts of 2 stroke S.I. engines?
28/06/11
What happens if the piston gap is too big?
What happens if the piston gap is too small?
How does a 2 stroke diesel engine work?
What is happening below and above the piston?
Explain what is meant, by scavenging when applied to 2 stroke SI engines?
Why must roller and ball race bearings be used on 2 stroke SI engine crankshafts?
Why are rollers caged in crankshaft bearings?
Why must ‘split’ type bearings be used on one piece crankshafts?
Why do we have pins between the piston ring gaps on a 2 stroke?
How does a reed valve work on a two stroke?
How do you check a reed valve?
Explain the term ovality and taper and how are they formed?
How does the piston rings seal in the bore?
What is meant by the terms groove depth, side clearance and end gap on the pistons rings?
Explain the difference between a 2 stroke and a 4 stroke engine?
What is meant by each of the following terms:
(a) Mechanical Efficiency(b) Thermal Efficiency(c) Volumetric Efficiency?
List 2 methods of lubricating the internal parts of 2 stroke S.I. engines? Premix - with the fuel 250ml oil to 1L petrol. Oil injection, a hose from the oil pump feeds to the space where the venturi meets the reed valve which is then delivered into the boar.
What happens if the piston gap is too big?
What happens if the piston gap is too small?
How does a 2 stroke diesel engine work?
Wednesday, June 15, 2011
DIESEL
Who invented the diesel engine and when? In 1893 by Rudolf Diesel

What fuel pressure would you get from a diesel pump? 15 psi - 18 psi in the new engines
How does the diesel pump work and why do we need to time the pump? The pump has to be timed so it delivers fuel at the right time and not for example when the piston is a BDC. The pump runs straight off the crank shaft so as the motor is running more slowly it pumps less fuel and when it is pushed to go faster the pump pumps more fuel to the engine.

How do you time the pump and with what equipment would you use? To time the pump you start by taking of the cam belt then lining up the notches in the sprockets with the marks on the block, once this is gone put the belt back on making sure the marks are still lined up. Now use the DTI gauge to set the motor to specifications. (sometimes you have to take off the pump to get the cam belt off).

What is the purpose of a glow plugs and how do you test the circuit? Glow plugs heat the air so it is hotter than the outside temperature, at this point it has also expanded because of the heat which would make the diesel ignite more effectively as a result of a more compression. You can test the each plug by measuring the resistance there is through each glow plug using a multimeter (if it reads approximately less than 5 ohms the plug is not defective). You can also test it straight from the battery (using jumper leads) if it works the plug will glow like a hot element.

Why do we need an lift pump on diesel engine? to supply/feed the diesel pump with fuel so there is no unnecessary stress on the diesel pump to pull and push fuel.
Why do we need a electronic fuel shut of valve? So that in a emergency there is a much lower chance of an explosion because there is no fuel traveling near exposed sparks etc
What is the knock sensor for and where is it situated? The knock sensor works by simply retarding the timing until the detonation stops. There is a significant decrease in power as it retards it also saves the engine from detonation which will break pistons and burn up head gaskets, The knock sensor is usually on high compression engines e.g. turbo's, performance cars and diesels an is located on the bloch of all cars.

How does the diesel injectors work? The fuel is delivered to the injector at a low pressure (5 -10 psi) by the diesel pump, once there it is pressurised to 2000 - 6000 psi, once the pressure is high enough it sprays into the compression chamber. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JgbuE1FT5Ks
Why do you need to bleed a diesel engine after replacing a fuel filter or removing the pump? Because air pockets might occur making it hard to start and could damage your starter motor.
How do you bleed the system? Pump the big primer button before you unscrew the metal fuel lines just a little bit so that the fuel can escape. Turn the engine over but don't start it until you see fuel spray from the base of the lines where the are screwed down.
How does a turbo work? A turbo runs straight from the exhaust which spins
Why do we need a turbo fitted to a diesel engine? Mainly to improve peformance because diesels are such torquie engines you wouldn't get much speed at high revs, more fuel and air adds alot more speed.

What is a supercharger? This is pretty much a air compressor because more fuel and more air = more power they are belt, chain or gear driven so power to the wheels from the throttle is instant.
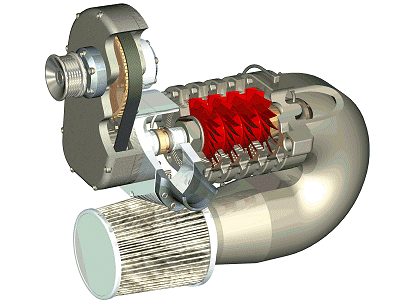
Whats the difference between a turbo and supercharger? A super charger uses belt or chain driven pulleys to force more air and fuel into the combustion chamber, it also takes horsepower to make horsepower so there is no lag. A turbo charger takes pressure from the exhaust to spin a turbine which compresses and forces more air into the engine. Because a turbo runs off the exhaust is doesn't use any horsepower from the engine to make more, the only down side to a turbo is the lag as it winds up.
Why do we need a after- cooler or inter-cooler fitted to a diesel engine? The air coming from the exhaust is hot so it is ppushed through an intercooler which cools the temp, the turbo then force feeds the engine with more air. Because the air is cold is is more dense so even more oxygen is therefore in the bore getting compressed.

What the difference between in a direct-injection ( DI,) an indirect-injection ( IDI)? D.I has the injector spraying "directly" into the bore so it can be compressed by the piston at TDC resulting in ignition. I.D.I injects the fuel in a mixing/swirl chamber just above the bore with the glow plug which is then compressed.


What is the purpose of an governor? There are hydrolically, pneumatic and mechanical governors all of them do the same job which is to control the engines idol speed and top speed.

What is the difference between a diesel and a common rail diesel? A diesel engine is mechanically timed and has much less pressure in the fuel rail, a common rail diesel engine has very high pressure through the fuel rail and everything is electronically controlled and monitored making it more efficient and more powerful.

http://www.freeengineinfo.com/knock-sensor.htm
http://www.ehow.com/how_5183612_test-glow-plugs.html
www.wikipedia.com
Perrin Robinson
Ricardo Macedo
What fuel pressure would you get from a diesel pump? 15 psi - 18 psi in the new engines
How does the diesel pump work and why do we need to time the pump? The pump has to be timed so it delivers fuel at the right time and not for example when the piston is a BDC. The pump runs straight off the crank shaft so as the motor is running more slowly it pumps less fuel and when it is pushed to go faster the pump pumps more fuel to the engine.
How do you time the pump and with what equipment would you use? To time the pump you start by taking of the cam belt then lining up the notches in the sprockets with the marks on the block, once this is gone put the belt back on making sure the marks are still lined up. Now use the DTI gauge to set the motor to specifications. (sometimes you have to take off the pump to get the cam belt off).

What is the purpose of a glow plugs and how do you test the circuit? Glow plugs heat the air so it is hotter than the outside temperature, at this point it has also expanded because of the heat which would make the diesel ignite more effectively as a result of a more compression. You can test the each plug by measuring the resistance there is through each glow plug using a multimeter (if it reads approximately less than 5 ohms the plug is not defective). You can also test it straight from the battery (using jumper leads) if it works the plug will glow like a hot element.

Why do we need an lift pump on diesel engine? to supply/feed the diesel pump with fuel so there is no unnecessary stress on the diesel pump to pull and push fuel.
Why do we need a electronic fuel shut of valve? So that in a emergency there is a much lower chance of an explosion because there is no fuel traveling near exposed sparks etc
What is the knock sensor for and where is it situated? The knock sensor works by simply retarding the timing until the detonation stops. There is a significant decrease in power as it retards it also saves the engine from detonation which will break pistons and burn up head gaskets, The knock sensor is usually on high compression engines e.g. turbo's, performance cars and diesels an is located on the bloch of all cars.
How does the diesel injectors work? The fuel is delivered to the injector at a low pressure (5 -10 psi) by the diesel pump, once there it is pressurised to 2000 - 6000 psi, once the pressure is high enough it sprays into the compression chamber. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JgbuE1FT5Ks
Why do you need to bleed a diesel engine after replacing a fuel filter or removing the pump? Because air pockets might occur making it hard to start and could damage your starter motor.
How do you bleed the system? Pump the big primer button before you unscrew the metal fuel lines just a little bit so that the fuel can escape. Turn the engine over but don't start it until you see fuel spray from the base of the lines where the are screwed down.
How does a turbo work? A turbo runs straight from the exhaust which spins
Why do we need a turbo fitted to a diesel engine? Mainly to improve peformance because diesels are such torquie engines you wouldn't get much speed at high revs, more fuel and air adds alot more speed.
What is a supercharger? This is pretty much a air compressor because more fuel and more air = more power they are belt, chain or gear driven so power to the wheels from the throttle is instant.

Whats the difference between a turbo and supercharger? A super charger uses belt or chain driven pulleys to force more air and fuel into the combustion chamber, it also takes horsepower to make horsepower so there is no lag. A turbo charger takes pressure from the exhaust to spin a turbine which compresses and forces more air into the engine. Because a turbo runs off the exhaust is doesn't use any horsepower from the engine to make more, the only down side to a turbo is the lag as it winds up.
Why do we need a after- cooler or inter-cooler fitted to a diesel engine? The air coming from the exhaust is hot so it is ppushed through an intercooler which cools the temp, the turbo then force feeds the engine with more air. Because the air is cold is is more dense so even more oxygen is therefore in the bore getting compressed.
What the difference between in a direct-injection ( DI,) an indirect-injection ( IDI)? D.I has the injector spraying "directly" into the bore so it can be compressed by the piston at TDC resulting in ignition. I.D.I injects the fuel in a mixing/swirl chamber just above the bore with the glow plug which is then compressed.


What is the purpose of an governor? There are hydrolically, pneumatic and mechanical governors all of them do the same job which is to control the engines idol speed and top speed.

What is the difference between a diesel and a common rail diesel? A diesel engine is mechanically timed and has much less pressure in the fuel rail, a common rail diesel engine has very high pressure through the fuel rail and everything is electronically controlled and monitored making it more efficient and more powerful.

http://www.freeengineinfo.com/knock-sensor.htm
http://www.ehow.com/how_5183612_test-glow-plugs.html
www.wikipedia.com
Perrin Robinson
Ricardo Macedo
Wednesday, June 8, 2011
FUEL INJECTION
ECU- Electronic control unit? The ECU is like the brain of the engine it sends and receives messages of what the motor is doing, it controls and monitors the rest of the minor sensors, changing things like air flow and fuel mixtures to make the engine run to the ideal specifications.

Mass air flow sensor? It monitors how much air is entering the system then sends the message to the ECU so the amount of fuel to air mixture is right
Air Temp sensor? This is a very important sensor in the (car) because depending on the density/temp of the air the amount of fuel has to be changed because otherwise the fuel mix might be to lean or to rich - Hot, light air, less fuel needed. Cold, dense air, more fuel needed. If the motor is running wrong mixtures you might end up fouling the spark plug, consuming to much petrol or have a lack in power.
TPS throttle position sensor? This is located on the butterfly shaft and sends the ECU info about the position so it can monitor how much fuel to be injected etc
Throttle body? To control the amount of air taken into the engine.
Temp sensor? Tells us when the engine is cold and hot

fuel rail? The fuel rail is mounted next to the injectors and its purpose is to deliver equally pressurised fuel to the injectors.

Fuel pressure regulator? Is to maintain a constant fuel pressure above the intake manifold pressure.
Injectors? Injectors spray a mist of fuel into the cylinder

Idle air control? The idle air control is to change the engine idle RPM by opening and closing an air bypass channel inside the throttle body.
O2 sensor ( lambda sensor)? Measures the amount of oxygen is being used in the engine, which the determines if the engine runs lean or rich.
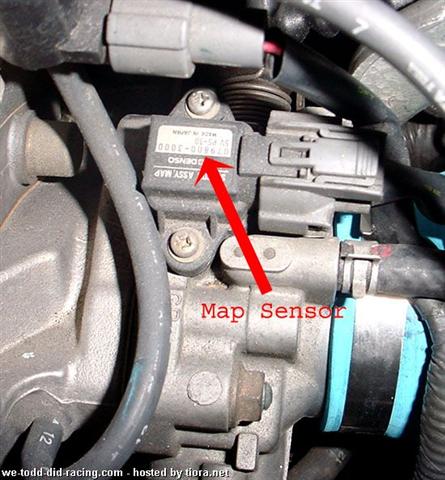
Map sensor? The map sensor reads the manifolds constant and instant pressure so it can determine the air density which is then sent to the ECU.

Plenum chamber? The plenum chamber is to equalise pressure entering the motor for more even distribution. A plenum chamber can also work as a silencer device.

Camshaft & Crankshaft sensor? These sensors tell the ECU where the shaft is in its rotation, this then determines when the fuel is delivered and when the spark is set.
Who invented fuel injection and when? The inventor of fuel injection was Herbert Akroyd Stuart in 1885.
Explain how an single and multi injection system works? Single - is a petrol injection point where the fuel and air is mixed by one centraly positioned injector. the injector is mounted on the throttle body and injects the fuel on top of the throttle to be sucked into the boar.
Multi - Uses one injector for each piston. the injectors are mounted on the intake manifold and inject the fuel into the top of the boar.
What does EFI stand for? Electric fuel injection
REFERENCES
http://ricardodemacedoengineer.blogspot.com/
www.wikipedia.com

Mass air flow sensor? It monitors how much air is entering the system then sends the message to the ECU so the amount of fuel to air mixture is right
Air Temp sensor? This is a very important sensor in the (car) because depending on the density/temp of the air the amount of fuel has to be changed because otherwise the fuel mix might be to lean or to rich - Hot, light air, less fuel needed. Cold, dense air, more fuel needed. If the motor is running wrong mixtures you might end up fouling the spark plug, consuming to much petrol or have a lack in power.
TPS throttle position sensor? This is located on the butterfly shaft and sends the ECU info about the position so it can monitor how much fuel to be injected etc
Throttle body? To control the amount of air taken into the engine.
Temp sensor? Tells us when the engine is cold and hot
fuel rail? The fuel rail is mounted next to the injectors and its purpose is to deliver equally pressurised fuel to the injectors.
Fuel pressure regulator? Is to maintain a constant fuel pressure above the intake manifold pressure.
Injectors? Injectors spray a mist of fuel into the cylinder

Idle air control? The idle air control is to change the engine idle RPM by opening and closing an air bypass channel inside the throttle body.
O2 sensor ( lambda sensor)? Measures the amount of oxygen is being used in the engine, which the determines if the engine runs lean or rich.
Map sensor? The map sensor reads the manifolds constant and instant pressure so it can determine the air density which is then sent to the ECU.

Plenum chamber? The plenum chamber is to equalise pressure entering the motor for more even distribution. A plenum chamber can also work as a silencer device.
Camshaft & Crankshaft sensor? These sensors tell the ECU where the shaft is in its rotation, this then determines when the fuel is delivered and when the spark is set.
Who invented fuel injection and when? The inventor of fuel injection was Herbert Akroyd Stuart in 1885.
Explain how an single and multi injection system works? Single - is a petrol injection point where the fuel and air is mixed by one centraly positioned injector. the injector is mounted on the throttle body and injects the fuel on top of the throttle to be sucked into the boar.
Multi - Uses one injector for each piston. the injectors are mounted on the intake manifold and inject the fuel into the top of the boar.
What does EFI stand for? Electric fuel injection
REFERENCES
http://ricardodemacedoengineer.blogspot.com/
www.wikipedia.com
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)